Primary Elementary Handwriting Instruction
At the primary elementary level, kindergarten through the second or third grade, handwriting instruction should focus on basic mechanics and motor skills, with an emphasis on mastering letter formation before demanding precision. Handwriting language should be used frequently with consistent auditory cues for letter formations, as well as pencil grip, posture, and paper position. Visual representations of properly formed letters should available and accessible to students. Fine motor activities are especially important for the development of proper grip and hand movement, as well the hand-eye coordination needed for precision. Large motor activities should also be included to increase the student's awareness of the stroke pattern used for letter formation.
Key Components:
- Stroke - The most common handwriting programs include 4 basic manuscript (print) strokes. These are horizontal lines, vertical lines, slants, and circles.
 |
| (image source: http://www.shenet.org/arongen/jpeebles/jpdocs/BasicStrokes.gif) |
- Pencil Grip, Posture and Paper Placement - There are some variations among curricula as to what is correct, but in general the pencil should be help with the first to fingers and thumb, the paper should match the angle of the writing arm, and writers should be taught to sit up straight and not lay on their desk or twist their body while writing.
MKHolder.gif) |
| Proper posture, paper position, and grip for left-handed writing (Image Source: http://handedness.org/action/leftwrite.html) |
- Letter Formation - Consistent language should be used for teaching letter formations. This includes auditory cues that match arrows and starting points on visual displays.
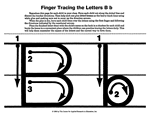 |
| (Image Source: http://i.infopls.com/images/tv/printables/Krause_0-87628-149-8_38.gif) |
- Spacing - Includes the spacing between letters within words and the spacing between words
 |
| (image source: http://www.hwtears.com/files/images/learn-and-check.jpg) |
- Handwriting activities that involve the four basic strokes outside of letter formation are excellent for developing motor memory. Provide students with lots of opportunities to freely use crayons, markers, pencils, pens, chalk, etc. with the goal of increasing student's awareness and use of handwriting strokes, not just letter formations. One example would be drawing a square house with a triangle roof and putting a round window on the front.
 |
| (Image Source: http://preschoolprintables.info/347/writing-patterns/) |
- Clay and play-dough activities help strengthen the hand muscles used for handwriting. To make the activities meaningful to handwriting instruction, have students form letters with small balls or ropes of play-dough.
 |
| (image source: http://shopping.hwtears.com/product/Roll-A-Dough_Letters/prek) |
- To teach spacing between words and standard lined paper, have students measure the gap with the width of their index finger, or use a word spacing tool such as the Bookworm Word Spacer available from Oriental Trading Co. For larger paper and other writing surfaces, appropriately scaled objects can be used for students to assess their word spacing, such as round/square magnets, checkers, cotton balls, etc.
Upper Elementary Handwriting Instruction
At the fourth grade level, the handwriting for many students has become automatic, but that does not mean that handwriting instruction should be halted. Refined, legible strokes and speed should become the focus so that handwriting can be used effectively for a variety of assignments and purposes. This is especially important as content area instruction becomes more rigorous. Students are now taking more notes, writing more essays, and sharing greater amounts of information with others. Such tasks need to be legible, as in readable with proper size and spacing between letters and between words, in order to be an effective means of communication. They also need to be completed in a timely manner to ensure successful completion of curricula objectives and educational goals.
A student's execution of handwriting skills should also continued to be assessed. Quite often, problems with speed and legibility can result from execution errors, such as improper pencil grip, posture, and paper placement. For more information about handwriting execution, refer to Handwriting Components for Primary Elementary Handwriting Instruction above.
Key Components:
- Speed - How quickly a student can write words or passages accurately becomes increasingly important as students progress in grade level requirements.
- Legibility - The readability of a written work, to include proper letter size and spacing both within and between words. This is particularly in upper elementary as students take more notes they will need to be able to read later as well as use their handwriting to share greater amounts of information. However, distinctions can be made between the legibility requirements for various tasks, such as allowing messy handwriting for lecture note taking, but not for thank you notes.
- Execution - The appropriate use letter strokes, posture, and pencil grip for efficient writing should be emphasized until the student displays mastery.
- The best way to improve handwriting speed and frangibility is practice. However, handwriting activities in upper elementary need to be meaningful to ensure students will put forth their best efforts. Having a daily writer's workshop or journal time with students self-selecting their writing topics is one way to provide students with practice. When evaluating handwriting, focus should be on one or two elements at a time. For instance, if a students work displays difficulties with word spacing and also capital letter size, focus on remediating one of these areas at a time.
 |
| (image source: http://www.scholastic.com/teachers/node/216613) |
- At upper elementary, handwriting can easily be integrated into other content area instruction. One simple way to do this is to include handwriting neatness as a criteria on essay or project rubrics and provide students with self-assessment measures.
Resources for Handwriting Components and Strategies
Common Core State Standards
To access the Common core State Standards for handwriting, refer to the Conventions of Standard English beginning on page 26.
Common Core Standards Initiative. (2010). Language standards K-5: Conventions of standard English. Common Core State Standards for English Language Arts & Literacy in History/Social Studies, Science, and Technical Subjects. Retrieved from: http://www.corestandards.org/assets/CCSSI_ELA%20Standards.pdf
Six Questions Educators Should Ask Before Choosing a Handwriting Program
This ERIC digest document discusses historical and developmental aspects of handwriting instruction.
ERIC Development Team. (1997). Six questions educators should ask before choosing a handwriting program. ERIC Digest. Bloomington, IN: ERIC Clearinghouse on Reading English and Communication. (ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED409589). Retrieved from: http://www.eric.ed.gov/PDFS/ED409589.pdf
Teaching Left-Handers to Write
Prepared for the Handedness Research Institute, this article explores the distinctions between left-handed and right-handed handwriting instruction.
Holder, M.K. (2003). Teaching left-handers how to write. Handedness Research Institute papers. Retrieved from: http://handedness.org/action/leftwrite.html
What's Normal, What's Not
"This article lists some milestones to look for as your child's handwriting skills begin to develop. The article also describes some signs and symptoms of dysgraphia, a learning disability that affects a child's handwriting and ability to hold a pen, pencil, or crayon."
Reading Rockets. (2008). Handwriting: What's normal, what's not. Reading Rockets. Washington, DC: WETA. Retrieved from: http://www.readingrockets.org/article/28252/
The Importance of Teaching Handwriting
Written by Dr. Louise Spear-Swerling for LD OnLine, this article discusses handwriting instruction for the learning disabled community, though much of the content is relevant to all learners. LD OnLine is an educational service of public television station WETA in Washington, D.C, and works in association with the National Joint Committee on Learning Disabilities.
Spear-Swerling, L. (2006, August). The importance of teaching handwriting. LD OnLine. Retrieved from: http://www.ldonline.org/spearswerling/The_Importance_of_Teaching_Handwriting

